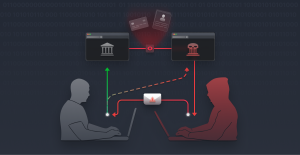
Security misconfiguration is any error or vulnerability present in the configuration of code that allows attackers access to sensitive data. There are many types of security misconfiguration, but most present the same danger: vulnerability to data breach and attackers gaining unauthorized access to data.
Security misconfiguration, because it involves flaws in security configuration, can lead to a data breach and even complete system compromise. Depending on the value of the data compromised, this can have a significant negative impact on a business. Attackers may be able to exploit or even modify parts of applications by taking advantage of security misconfigurations. These security misconfiguration vulnerabilities leave a business exposed to potential attack.
Some concrete examples of security misconfigurations include AD misconfigurations, vulnerabilities within the Active Directory domain. These common security misconfigurations range from attackers gaining administrative privileges to issues arising from services running on hosts with multiple administrators.
Another example is a security misconfiguration that was discovered in JIRA, a collaboration tool. One misconfiguration exposed many companies to the vulnerability of releasing corporate and personal data. In this case, it was an authorization misconfiguration in Global Permissions that caused the security risk. These are only two of the many kinds of security misconfiguration that can affect a business.
Security misconfiguration occurs when security settings are put in place poorly, or not implemented at all. Cloud misconfiguration and identity service misconfiguration both stem from improper security configuration.
There are several types of security misconfiguration that can affect a business.
1). AD misconfiguration, which exposes administrator and domain credentials.
2). Identity access misconfiguration, which provides attackers easy access to applications.
3). API security misconfiguration, which leaves unrestricted endpoints and unprotected files.
4). Network security misconfiguration, which is incorrect configuration of an information system.
5). Cloud security misconfiguration, which leaves gaps in the cloud environment that may lead to security breach.
6). Web server misconfiguration, which often includes unnecessary default and sample files.
Any aspect of an application or code that should have security measures is susceptible to security misconfiguration.
Security misconfiguration can occur in many ways. Some of the common causes include:
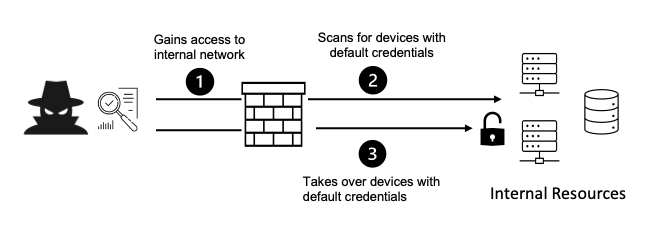
Security misconfiguration can expose a business to higher risk of attack, and when attackers gain access, it can lead to major impact on the business. The risks of security misconfiguration vary depending on the data that is exposed. Big or small, security misconfiguration can cause a business to lose money, customers and reputation.
The overarching risk of security misconfiguration is exposing systems, services or data to attackers. Different types of attacks pose different levels of risk. In a directory traversal attack, adversaries gain unauthorized access to browse file structure and discover vulnerabilities. They can potentially modify parts of an application, and in some cases reverse engineer it, causing significant loss for a business.
Other misconfigurations, such as those present in firewalls or unused administration ports, expose a business to vulnerability of a remote attack. Cloud misconfiguration can lead to application access for attackers and poses other security risks depending on what data a business stores in the cloud. Security misconfiguration exposes a business to risks which have immediate and lasting impact.
When sensitive data is leaked or stolen by an attacker, the result can mean potential loss of customers, regulatory fines for failing to meet required security measures, and harm to finances and reputation. In addition, any business-critical information gained by an attacker can put a business at further risk. The access gained via security misconfiguration flaws can also lead to complete system compromise.
Any breach of data or applications can slow down a business and, in some cases, bring production to a halt. The greater the protection needs of an application or data that is exposed, the worse the impact on a business. That’s why preventing security misconfiguration is vital.
Improve System Visibility
Use network diagrams to map your infrastructure and understand how systems connect.
Implement asset inventory tools to track devices, apps, and services.
Enable logging and monitoring to detect unexpected behavior.
Use Security Scanning Tools
Deploy automated security scanners (e.g., Nessus, OpenVAS, Nikto) to detect misconfigurations like open ports, outdated software, or weak permissions.
Run container and cloud configuration scans using tools like AWS Config, Azure Security Center, or Kube-Bench.
Conduct Internal Testing
Perform configuration reviews regularly to ensure all systems comply with organizational policies.
Use checklists or hardening guides (like CIS Benchmarks) to verify security settings.
Employ vulnerability assessment tools to simulate common attack paths.
External Penetration Testing
Hire external cybersecurity professionals to simulate real-world attacks and uncover misconfigurations that internal teams might miss.
These tests reveal external exposure risks, especially in web applications and network boundaries.
Perform Code and Infrastructure Reviews
Review Infrastructure as Code (IaC) (e.g., Terraform, Ansible) scripts for insecure configurations.
Conduct static code analysis to find insecure defaults or hardcoded secrets.
Enable Continuous Monitoring
Set up SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems to collect and analyze logs for signs of misconfiguration.
Use real-time alerting to react quickly to configuration drift or changes.
Benchmark Against Standards
Compare system configurations against standards such as NIST, ISO 27001, or OWASP Secure Configuration Guidelines.
Use compliance tools to report on gaps and areas of risk.
Train and Update Teams
Regularly train staff on secure configuration practices.
Keep documentation up-to-date and enforce change control policies.
Security misconfiguration is a vulnerability for any business. These misconfigurations are caused by poorly implemented or non-implemented security features and can deal lasting harm to a business. With proper diagnostics and prevention, businesses can reduce the risk posed by security misconfiguration.
The CrowdStrike Falcon® platform can help prevent and diagnose security misconfigurations by ensuring strong security measures are implemented across a business’s code and applications.
Read More :
Signup our newsletter to get update information, news, insight or promotions.
Copyright 2025 © Hackanics